Demystifying DRaaS: Your Comprehensive Guide
Published: December 19, 2022
By Gene Everette

What is Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS)?
Disaster recovery is the process and methodology by which a company regains access to its IT infrastructure after a disaster. Disasters can be caused naturally (i.e. Earthquake, Wind, Fire, etc.), or by equipment failure (storage drive failure, server failure, power outage, internet outage, etc.) or by Cyber terrorism (disgruntled employee, Malware, Ransomware, etc.). Whatever the cause, the result is the same: the IT infrastructure goes down, it must be mitigated and recovered to maintain business continuity.
Due to recent advances in immutable snapshot technology, companies that provide Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) can also now provide DRAAS solutions as an affordable option for mid-market Enterprise. Nfina’s implementation of DR successfully implements the recovery portion of the NIST Cyber-Security Standard. This significantly reduces recovery time objectives (RTOs) and ensures that the business can resume operations within minutes rather than hours or days.
One of the main benefits of DRaaS is its flexibility. Unlike traditional disaster recovery solutions that require costly infrastructure investments and complex setups, DRaaS solutions eliminate these requirements by leveraging cloud computing technology. This means that businesses no longer must worry about managing physical hardware or maintaining backup servers at off-site locations. Instead, they can simply pay for the services they need based on their specific requirements.
DRaaS also eliminates the risk associated with managing complex disaster recovery processes internally. The responsibility falls on the DRaaS provider who has expertise in handling disaster recovery situations effectively. They use advanced technologies like continuous data protection (CDP), virtualization techniques like hypervisors or containers along with automated failover procedures to ensure minimal disruptions during a disaster.
How is DRaaS Implemented?
One of the main reasons why DRaaS has become increasingly important in today’s digital age is due to the rise of cyber threats. With hackers becoming more sophisticated and targeted in their attacks, no business is immune from potential cyber-attacks. In fact, according to IBM’s 2021 Cost of a Data Breach Report, the average cost of a data breach for companies worldwide was $4.24 million – an increase of nearly 10% since 2019.
Disaster recovery as a service relies upon the geographic redundant replication of data far enough away from the primary site so as not to be affected by the disaster. In most instances, 600-1000 miles away is often recommended as a best practice for this purpose. When the infrastructure goes down (for whatever the reason), the business needs to recover lost data from a second location where the data is backed up.
A backup is a very crude form of disaster recovery, but its RPO (Recovery Point Objective) is usually insufficient for most organizations to avoid financial losses. This is because the typical backup schemes are very compute and I/O intensive and can only be run daily (typically after hours) and will result in subsequent data loss (up to 24 hours) if restoration is necessary.
For a disaster recovery process to work efficiently and minimize data loss, the system should be designed to duplicate compute and storage resources and keep them synchronized with an active-active replication scheme to minimize downtime. This active-active scheme must also be reversable to maintain maximum protection while running out of the DR site.
Disaster Recovery Planning
So how does one go about creating an effective Disaster Recovery Plan? Let’s break it down into key steps:
1. Risk Assessment: The first step is to identify potential risks and their impact on your business. This could include natural disasters specific to your location (e.g., earthquakes), human-made threats (e.g., cyberattacks), or internal issues (e.g., hardware failure).
2. Business Impact Analysis: Once you have identified potential risks, assess how each would impact your organization’s critical functions such as communication systems, customer service, sales operations etc.
3. Prioritization: After identifying critical functions, determine which ones need immediate recovery efforts in case of a disaster.
4. Define Recovery Objectives: Set specific recovery objectives for each function based on its priority level – this could range from minimal disruption for low-priority functions to complete restoration within hours for high-priority ones.
5. Develop Strategies: Based on the recovery objectives set above, develop strategies for restoring operations – this could include having redundant systems in place or moving operations to alternate locations.
6. Document the Plan: Once strategies are developed, document the entire plan in detail, including emergency contact information and step-by-step procedures.
7. Test and Update Regularly: It is crucial to test the plan regularly to ensure its effectiveness. Also, remember to update it as your business evolves.
Having a Disaster Recovery Plan in place is not just good practice but also essential for businesses of all sizes.
RTO and RPO in DRaaS
RTO, or Recovery Time Objective, is the maximum amount of time it takes for an organization to restore its systems, applications, and data after a disaster strikes. In simple terms, it is the time frame within which an organization must resume normal operations without incurring significant losses. It is typically measured in hours or days and varies based on business needs and criticality of systems.
On the other hand, RPO, or Recovery Point Objective, refers to the maximum acceptable amount of data loss during a disaster. It indicates how much data an organization can afford to lose before it significantly impacts their operations. For instance, if an organization has an RPO of four hours and experiences a system failure at 2 PM; then it means they can only afford to lose data up until 10 AM before it starts affecting their business operations.
Both RTO and RPO are essential metrics that need careful consideration while designing a disaster recovery plan using DRaaS. Organizations must determine these metrics based on their business requirements and operational capabilities.
When selecting a DRaaS provider, businesses should ensure that their chosen service level agreements (SLAs) align with their RTOs and RPOs. This ensures that they can meet their recovery objectives effectively without experiencing any significant downtime or data loss during disasters.
Benefits of DRaaS
1. Reduced Downtime: The biggest benefit of DRaaS is its ability to minimize downtime in case of a disaster. Traditional disaster recovery methods can take hours or even days to restore data and resume operations, leading to significant financial losses and damage to its reputation. With DRaaS, however, businesses can get back up and running within minutes, ensuring minimal impact on their operations.
2. Cost-Effective: Implementing traditional disaster recovery strategies can be expensive due to the need for hardware, software licenses, and dedicated staff. On the other hand, DRaaS eliminates these costs by utilizing cloud resources on a pay-per-use basis. This allows businesses to save money while still having access to top-notch disaster recovery solutions.
3. Scalability: One of the key advantages of using DRaaS is its scalability. As your business grows and evolves, you may need more robust disaster recovery solutions. With traditional methods, upgrading would require additional investments in hardware and software licenses. However, with DRaaS, scaling up is as simple as increasing your subscription plan with your service provider.
4. Simplified Management: Managing traditional disaster recovery systems can be complex and time-consuming for IT teams who are already burdened with daily tasks. With DRaaS, all aspects of disaster recovery are managed by the service provider – from backups to testing procedures – freeing up valuable time for IT professionals to focus on other critical tasks.
5. Reliable Data Protection: In today’s digital age where data is one of the most important assets for businesses, protecting it from potential disasters is crucially important. DRaaS ensures that your data is backed up and stored in secure, off-site locations, reducing the risk of data loss due to natural or man-made disasters.
6. Quick and Easy Implementation: Unlike traditional disaster recovery methods that require significant time and effort to set up, DRaaS can be implemented quickly and easily. This is because it leverages cloud-based services, eliminating the need for complex installations and configurations.
Key Features and Components of a DRaaS Solution
1. Real-Time Replication: One of the main features of DRaaS is real-time replication, which ensures that all changes made to your data are automatically backed up in real-time. This means that even if your primary system goes down, you will have access to the most recent versions of your data.
2. Automated Failover: In case of an outage or disaster scenario, DRaaS solutions offer automated failover capabilities that allow for seamless transition to backup systems without any disruption to business operations. This ensures minimal downtime and maximum uptime for your business.
3. Flexible Recovery Options: DRaaS providers offer flexible recovery options depending on the specific needs of your business. These options include full system restores, file-level restores, or virtual machine snapshots.
4. Scalability: As your business grows, so does the amount of data you generate and store. A reliable DRaaS solution should be able to scale with your business needs without compromising on performance or security.
5. Testing and Monitoring: To ensure the effectiveness of your disaster recovery plan, regular testing and monitoring are essential. Most DRaaS providers offer automated testing and monitoring services to ensure that your systems are constantly backed up and ready for any disaster.
6. Multi-Platform Support: In today’s digital landscape, businesses often use a combination of on-premises and cloud-based systems. A good DRaaS solution should be able to support multi-platform environments to cover all aspects of your business.
DRaaS vs BaaS
In this section, we will discuss the key differences between Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) and Backup as a Service (BaaS). While both services offer data protection and recovery solutions, they have distinct features that cater to different business needs.
1. Definition
DRaaS is a cloud-based disaster recovery solution that replicates and stores critical systems and data in an offsite location. In case of a disaster or outage, it enables businesses to quickly failover their entire infrastructure to the cloud and resume operations without any downtime. On the other hand, BaaS is a backup service that regularly backs up data to the cloud or an offsite location for safekeeping. It acts as a secondary copy of data in case of accidental deletion, corruption, or hardware failure.
2. Focus on Recovery Time Objective (RTO)
One of the main differences between DRaaS and BaaS is their focus on recovery time objective (RTO). RTO refers to the maximum acceptable duration of time within which systems must be recovered after an outage. DRaaS has a much lower RTO than BaaS as it aims to get businesses up and running within minutes by providing near-instant failover capabilities. This makes it ideal for companies that require high availability at all times, such as e-commerce websites or financial institutions. On the other hand, BaaS has longer RTOs ranging from hours to days depending on factors like internet speed and amount of data being restored.
3. Approach towards Failures
Another significant difference between DRaaS and BaaS lies in their approach towards failures. DRaas focuses on recovering entire systems while maintaining their configurations during disasters or outages. This ensures minimal disruption and allows businesses to continue functioning seamlessly from where they left off before the incident occurred.
On the other hand, BaaS primarily focuses on restoring specific files or folders from backups rather than entire systems. This means that in case of a disaster, businesses will need to rebuild their systems and reconfigure them before they can resume operations. This approach may result in longer recovery times and potential data loss.
4. Cost
The cost of DRaaS is generally higher than BaaS due to its more comprehensive coverage and near-instant recovery capabilities. Businesses must evaluate their RTO requirements and the criticality of their systems to determine if the extra cost is justifiable.
Cost of Downtime
The average downtime that organizations are experiencing is on the rise. Recent reports show a 16x increase. Recent surveys show that 91% of the IT executives polled estimate the average downtime of the IT ecosystem to be $300,000/hr, and 44% of those surveyed say it’s over $1M/hr for their respective companies. Since downtime is so expensive to bottom line, doesn’t it make sense to go beyond the traditional once a day backup and work with a DRaaS provider?
A Comprehensive DRaaS Solution with Nfina
Typically, a group of highly qualified technical staff members at Nfina will meet with the client to explore the current IT Ecosystem and propose a Disaster Recovery solution. The data exchanged usually includes a copy of the results from running the application RVTools. RVTools is a Windows .NET application which uses VMware vSphere Management SDK and CIS REST API to display detailed information regarding the customers IT Ecosystem.
Once the information is obtained about the client’s compute and storage environment, an offsite active-active quote is formulated to implement the DRasS solution. The three reference architectures that are typically deployed are shown below:
Single Node Hyperconverged Edge with DR

2-Node Hyperconverged Edge with HA
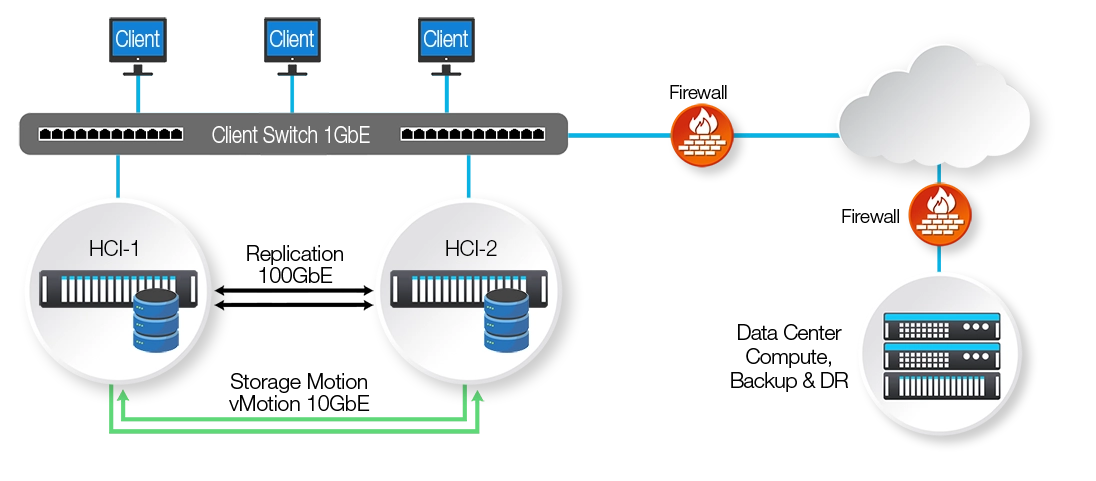
2-Node Hyperconverged Edge with HA

Conclusion
DRaaS coupled with hyperconverged technology is now very affordable, and with the advent of immutable snapshots that originate from the storage array, high frequency RTO/RPO policies can now be implemented. This technology allows recovery of the IT infrastructure within minutes (not hours or days), thus minimizing data-loss and downtime for the enterprise.
With the ever-increasing risk of disasters and data loss, businesses cannot afford to neglect the importance of disaster recovery planning. DRaaS Providers offer a reliable and cost-effective solution that ensures business continuity in times of crisis. It provides continuous data protection, flexibility, scalability, faster recovery times, and expert management services. Therefore, every business must prioritize implementing DRaaS as part of their disaster recovery strategy in today’s digital age.

At Nfina, our Eco-Friendly Solutions make it easy for our customers to achieve a lower carbon footprint for your disaster recovery as a service and play a positive role in bringing about a sustainable future. We design technologies and products to help people understand their impact and actions better.
Nfina’s Hybrid Cloud and Hyperconverged solutions provide energy efficiency by using high-density, lower-power VMs enabling our customers to scale their digital transformations sustainably by optimizing space, reducing power consumption, and lowering cooling and maintenance costs. Nfina is taking a leadership role in doing what it takes to tackle climate change.
Nfina has been carbon neutral for our operations since opening in 2012.

