What Is Hybrid Cloud?
Published: June 13, 2022
By: Gene Everette
What is Hybrid Cloud Computing?
Hybrid Cloud is a cloud computing Solution as a Service that consists of:
A private cloud that resides on-premisis (at the edge)
A public cloud that resides in a different geographic location (creating geo-redundancy)
An orchestration and administrative application that manages workloads between the private and public clouds, for ease of use from a single dashboard.
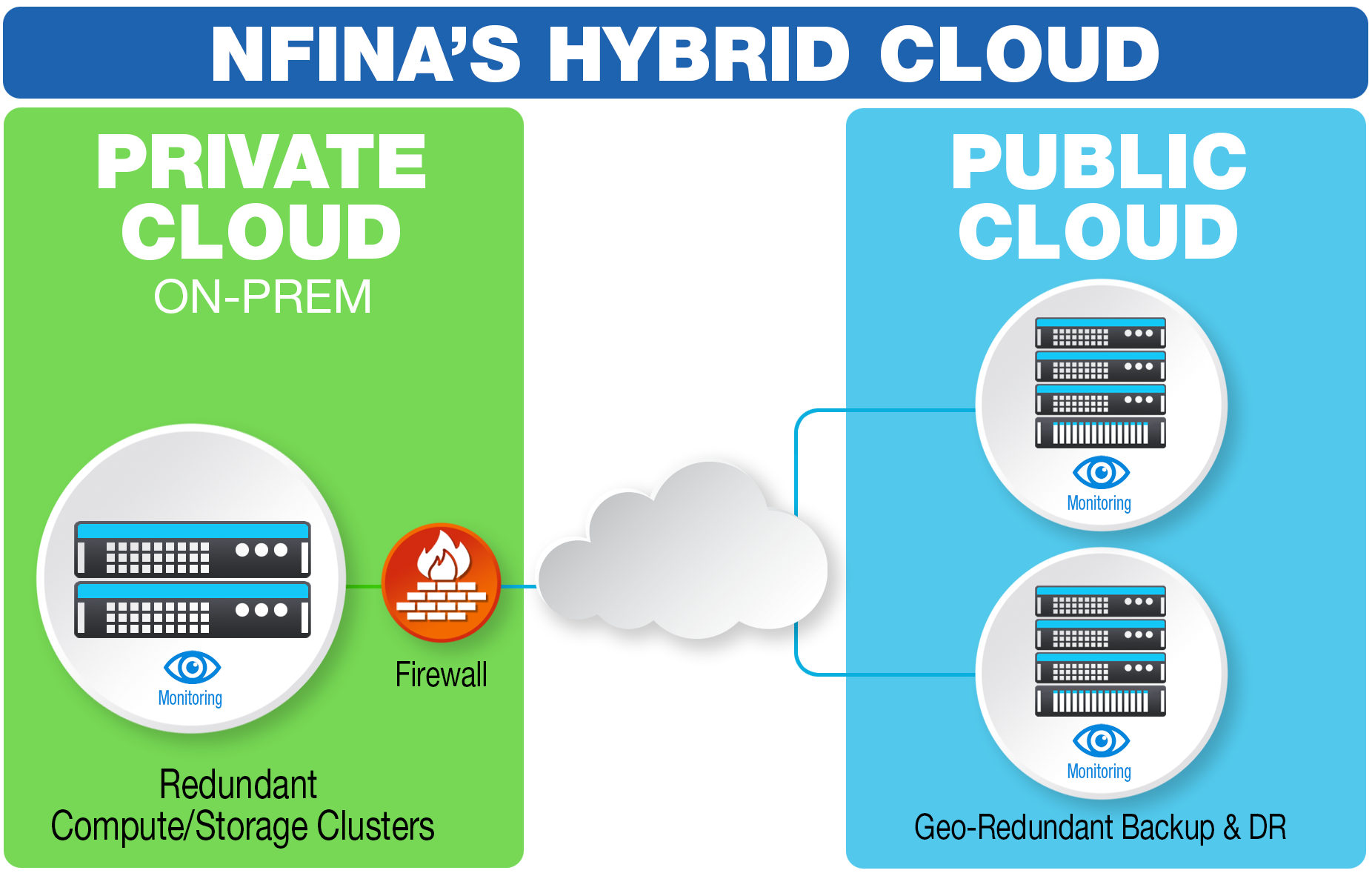
The Nfina Hybrid Cloud example: compute and storage cluster replicating to public facing cloud.
Hybrid Cloud Benefits:
There are many benefits of the Hybrid Cloud over traditional Cloud Computing or stand-alone private cloud. These include:
1. Workload agility:
Allows for Seamless Migration between sites as the business needs change.
Incremental Migration and Application Modernization allow you to move to the cloud at your pace.
Geographic Redundancy is built into the architecture.
Higher Performance allows you to put the apps requiring lower latency in the private cloud.
Cost Savings allows the user to shift workloads to the most cost-effective site.
Scalability allows for rapid cloud expansion if necessary.
2. Security – Allows for multiple copies in geo-redundant locations. It also allows well-vetted cyber-security solutions to be hosted on-premise as required for very sensitive data and certain regulated industries.
3. Backup and Disaster Recovery – Most Hybrid Cloud implementations will include geo-redundant data backup and disaster recovery options however geo-redundant computing options vary by vendor. Immutable snapshots ensure ransomware protection.
Is Hybrid Cloud the same as Multi-Cloud?
They are closely related but not exactly the same. Hybrid Cloud, by definition, has a shared public-facing cloud component. Multi-Cloud can include public cloud but usually refers to multiple private clouds (shown below) operating together to form a distributed IT Ecosystem that can orchestrate the benefits of Hybrid Cloud but done privately. It is highly desirable for users to have the same orchestration application capable of managing both Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud implementations. A Multi-Cloud implementation may be preferred by some users, especially if they have multiple edge campuses that can’t afford downtime. Perhaps the best of both worlds is the Private Multi-Cloud solution show below.

What is Hyperscale Cloud?
Hyperscale cloud is a form of public cloud that has been designed using object-oriented storage that can scale geo-redundantly (horizontally) and dynamically based on-demand.
Show More
This scale on demand feature is known as Elasticity. Elasticity uses docker containers (app and services bundled in a lightweight manner along with their dependencies and configuration) and Kubernetes (orchestration software designed to manage those containers and when and where they run). While this feature can reduce the expense of Enterprise or SaaS web hosting when the demand is very high (say millions of geographically diverse users), most small and mid-sized business infrastructures won’t need this capability. Therefore, even the experts agree that not everyone belongs in the public Hyperscale Cloud. If users have a fixed-sized infrastructure with a limited number of users, they will be paying for features they will never use or need in the hyperscale cloud implementations. Examples of Hyperscale cloud implementation include Azure, AWS, and Google clouds.
Migration via Snapshots
There are migration factors to consider when choosing a Hybrid Cloud or Multi-Cloud Vendor. Since workload agility is paramount, it must be easy and fast to move between on-site and off-site environments. Snapshot technology that can flow both ways (between public and private clouds) is required to ensure performance and re-synchronization are not impacted. Users don’t want to use traditional backup and restore functionality because snapshots should run frequently and be non-intrusive on the production computing. Furthermore, the snapshot technology used should be immutable (read-only) and encrypted (for cyber security reasons).
Hardware
When thinking about the cloud, users aren’t particularly thinking about the underlying hardware, firmware, and updates. That’s someone else’s problem, right? Not necessarily. In today’s Cyber-Security target-rich environments, security updates are essential. Keeping firmware and drivers up to date with changes to the OS, hard drives, Motherboard, BIOS, PCIe boards, adapters, firewalls, switches, RAID Cards, Network Adapters, etc., can be a daunting task if you are not an OEM or a Computer Engineer. These issues come into play when considering Hybrid Cloud and Multi-Cloud solutions.
Nfina’s Hybrid Cloud and Multi-Cloud Offerings
Nfina offers both Hybrid Cloud and private Multi-Cloud solutions, as well as a white glove implementation that includes: rack and stack, setup, validation, migration, and support, patch management, and remediation for the duration of the contract.
Show More
Since Nfina is an OEM, our world-class support staff will keep our Private Cloud and Public Cloud offerings running the latest firmware and Cyber-Security patches.
All Nfina public and private multi-cloud solutions support immutable snapshots for ultimate data protection from cybersecurity attacks, e.g. Ransomware.
The Nfina-View™ software is a SaaS orchestration application included in the solution that facilitates seamless management and migration of virtual computing environments for both Hybrid-Cloud and Multi-Cloud implementations. Nfina offers both private cloud and public cloud solutions that can provide significant savings for customers that don’t want to pay the premium of the Hyperscale Cloud.
Tips for Successful Hybrid Cloud Integration
Hybrid cloud integration is the process of combining and managing data, applications, and services from both on-premises and cloud environments. It offers various benefits such as flexibility, scalability, cost-efficiency, and improved performance. However, integrating these two distinct environments can be challenging and requires careful planning to ensure a successful implementation. In this section, we will discuss some essential tips for successful hybrid cloud integration.
Show More
1. Define Your Business Objectives: Before embarking on any hybrid cloud integration project, it is crucial to clearly define your business objectives. This includes understanding your organization’s current IT infrastructure, identifying the specific needs that the hybrid cloud infrastructure will address, and setting measurable goals for success. Having a clear understanding of your business objectives will help guide your decision-making process throughout the integration project.
2. Choose the Right Hybrid Cloud Service providers: When selecting cloud providers for your hybrid cloud infrastructure, it is essential to consider factors such as security measures, compatibility with existing systems, pricing models, and service-level agreements (SLAs). It is also crucial to choose providers that offer seamless integration solutions with other platforms or tools you are currently using.
3. Plan Your Integration Strategy: A well-defined integration strategy is critical for a successful hybrid cloud environment. This should include identifying which applications or workloads will be migrated to the cloud and how they will interact with on-premises systems. Additionally, consider factors such as data transfer methods between environments and how you will monitor and manage the entire environment.
4. Ensure Data Security: One of the most significant concerns with hybrid cloud services is data security across different environments. To ensure secure data transfer between on-premises and cloud systems, it is vital to implement robust encryption techniques while leveraging secure connections such as virtual private networks (VPNs) or dedicated leased lines.
5. Automate Where Possible: Automation plays a crucial role in streamlining processes in a hybrid environment while reducing errors caused by manual tasks. Consider using automation tools for tasks such as data migration, backup and recovery, and workload management. This can save time and resources while improving the overall efficiency of your hybrid cloud environment.
6. Regularly Monitor and Optimize: Hybrid cloud integration is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring to ensure optimal performance. It is essential to set up monitoring tools that provide visibility into all aspects of your hybrid environment, including application performance, resource utilization, and security. This will help identify any issues or bottlenecks before they impact critical business operations.
Best Practices for Managing Data in Hybrid Cloud Infrastructure
1. Understand your data requirements: The first step in managing data in a hybrid cloud environment is to gain a thorough understanding of your data requirements. This includes identifying the types of data you have, where it is stored, how frequently it needs to be accessed, and who needs access to it. This information will help you determine the best approach for storing and managing your data in the hybrid environment.
Show More
2. Implement a unified data management strategy: In a hybrid environment, different types of data may reside on different cloud platforms or on-premises systems. To avoid silos and ensure consistency, it is crucial to have a unified data management strategy that encompasses all these environments. This will enable seamless access and sharing of data across the entire infrastructure.
3. Utilize automation tools: Managing large volumes of data manually can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Automation tools can help streamline tasks such as backing up, replicating, and migrating data between different environments. They also ensure consistency and accuracy in managing large datasets.
4. Ensure strong security measures: Data security is paramount in any environment, especially when dealing with sensitive or confidential information. In a hybrid environment where there are multiple entry points for potential threats, implementing robust security measures such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular backups becomes even more critical.
5. Regularly back up your data: Backing up your data regularly is essential in case of system failures or cyber-attacks that could result in loss or corruption of important business information. It also provides an extra layer of protection against accidental deletion or overwriting of files by employees.
6. Institute proper data governance: With data spread across multiple environments, it is essential to have proper data governance policies in place to ensure compliance and regulatory requirements are met. This includes defining roles and responsibilities for managing data, establishing clear guidelines for data access and usage, and regularly auditing the system for any potential risks or vulnerabilities.
More information is available at: https://nfina.com/hybrid-cloud-security/

