Storage Clusters: Scaling Your Operations
Published: November 4, 2025
By: David Nicholson

What is a Storage Cluster?
A storage cluster is a group of interconnected servers that work together to store and manage data in clustered file systems. It provides a scalable, high-performance, and fault-tolerant solution for storing large amounts of information.
In a storage cluster architecture, multiple nodes are connected through a network protocol. These storage nodes can be physical or virtual machines with dedicated storage devices attached to them. The data is distributed across these storage nodes in such a way that if one node fails, the other storage nodes take over its workload.
This approach offers several benefits over traditional centralized storage solutions. For example, it allows businesses to add more capacity as needed without downtime or disruptions within distributed file system(s). Additionally, it improves performance by distributing the load across many file servers instead of relying on just one file server.
Using a storage cluster can help organizations become more agile in their data management while improving reliability and scalability at the same time.
Benefits of Using a Storage Cluster
Utilizing a storage cluster ensures data integrity by replicating information across multiple nodes in real time. This protects against accidental loss or corruption of critical data availability, ensuring businesses can operate securely knowing their information is safe and accessible at all times.
Increased Availability & Reliability |
With multiple nodes storing data, if one management node fails or experiences issues, the cluster can still function without interruption.
Scalability |
As storage needs grow, adding storage nodes to the cluster can take place seamlessly. This eliminates the need for costly hardware upgrades and provides organizations with more flexibility when planning for future growth.
Better Performance |
Storage clusters also offer better performance than traditional single-node operating systems by allowing to write data to be spread across multiple disks and servers simultaneously.
Faster Read/Write Speeds |
Storage clusters provide faster read/write speeds due to load-balancing algorithms that distribute requests evenly across all available storage nodes.
Simplicity |
Resources can be managed centrally through a single interface. This reduces complexity and streamlines operations while minimizing downtime during maintenance activities.
Enhanced Fault Tolerance |
By replicating data across multiple nodes, a storage cluster enhances fault tolerance. In the event of hardware failure or file system issues, the cluster storage can automatically route requests to functional nodes, minimizing disruptions.
Seamless Scalability |
Storage clusters offer seamless scalability, allowing organizations to expand their storage capacity easily. Additional nodes can be added to the cluster as needed, ensuring that storage can grow alongside the organization’s evolving requirements.
Simplified Management |
With a storage cluster, management becomes simplified due to centralized administration. Organizations can monitor and manage their storage resources through a single interface, making it easier to allocate and track storage area network usage.
Improved Disaster Recovery |
Storage clusters play a critical role in disaster recovery. By replicating data across multiple nodes, organizations can quickly recover from unexpected events such as hardware failures, natural disasters, or cyberattacks.
Efficient Resource Utilization |
Storage clusters optimize resource utilization by distributing data and workload evenly across nodes. This results in improved performance, reduced energy consumption, and increased overall efficiency.
Flexibility & Agility |
Storage clusters offer flexibility and agility in adapting to changing business needs. As storage requirements fluctuate, organizations can easily adjust the cluster configuration to meet new demands, ensuring seamless operations.
How do Storage Clusters Work?
Storage clusters are becoming increasingly popular as businesses strive to efficiently manage and store their growing amounts of data. These clusters are essentially a group of connected storage devices that work together to provide high availability, scalability, and performance for data storage.
-Shared Access |
This means that all servers in the cluster can read and write to the same pool of storage resources. This not only increases efficiency by reducing network traffic but also enables load balancing, where data can be distributed across multiple nodes for faster access. Shared access is made possible through specialized software or hardware components in the cluster that handle data locking and synchronization between different servers.
-Failover |
In a storage cluster, there are multiple servers that ensure dedication and transparency within the cluster. Once one server fails, fragments, or loses dedication, the servers can pivot to other nodes and pivot overlapping the failed work onto other nodes. Other nodes will be able to have dedication that ensures the work will be completed; however, there are servers that will be able to ensure no nodes or servers will break. Thus, providing consistency within the storage cluster with no single point of failure.
-Cluster Shared Volumes |
CSV or Cluster Shared Volumes technology enables multiple Microsoft cluster services to be bypassed. Each node can directly access the storage cluster for simultaneous access. This technology enables storage cluster layers to bypass traditional storage cluster technologies. Each node in the cluster has a unique perspective on the storage disks and can coordinate independently to execute commands. This minimizes conflict in the read/write processes on the disks.
–Storage dedicated networks |
Dedicated networks like Storage Area Network (SAN) and Network Attached Storage (NAS) serve nodes in a storage cluster for efficient communication. SANs utilize high-speed fiber channel or ISCSI connections, whereas NASs employ standard network protocols like SMB or NFS. These networks effectively enable servers to engage with the storage devices within the cluster, minimizing latency and enhancing performance.
How to Set Up a Storage Cluster
Setting up a storage cluster can be a daunting task, but with the right approach and tools, it can be achieved fairly easily. The first step is to choose your hardware and software components based on your specific needs. One of Nfina’s data storage consulting team members can help build the infrastructure that suits your company based current and future data usage, performance requirements, budget, and more.
Once you have selected your components, it’s time to configure them for optimal performance. This includes setting up network connections between two nodes and configuring the file system or object store layer of the cluster depending on which option was chosen earlier.
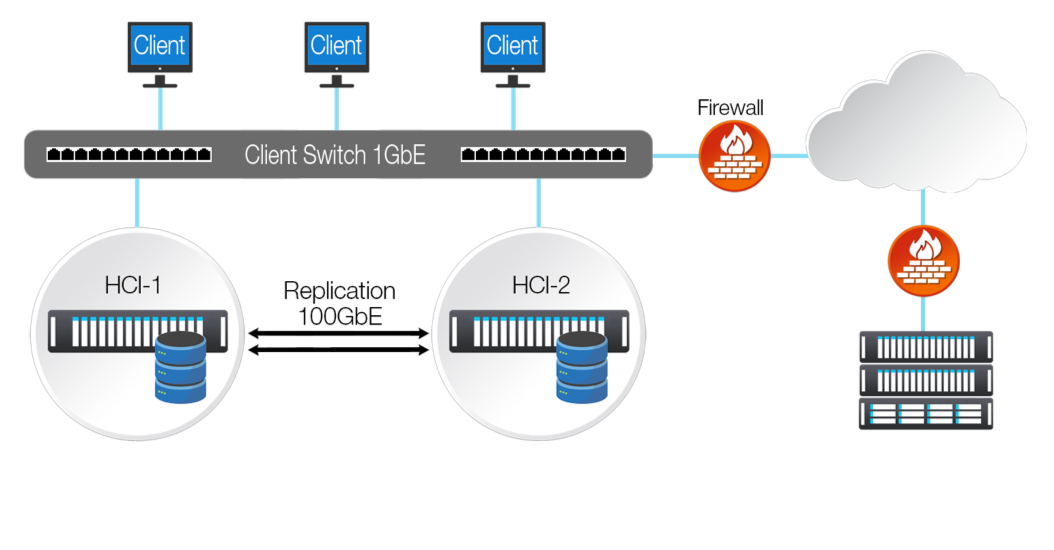
Next comes testing and validation to ensure that everything is working as expected. It’s important to test different scenarios such as management node failures or network outages so that you know how your cluster will react in these situations.
Once everything has been set up and tested successfully, it’s important to establish proper monitoring tools so that any issues can be detected quickly before they become critical problems.
Setting up a storage cluster requires careful planning and execution but with proper attention paid to each step of the process; you’ll end up with an efficient solution for storing large volumes of data across multiple nodes while ensuring redundancy and high availability.
Best Practices for Using & Maintaining a Storage Cluster
To maintain a storage cluster, you need to ensure that all the clustered file systems are running smoothly. One of the main tasks is monitoring and managing your nodes, which involves checking for any hardware failures or software issues that may arise. That’s where Nfina-View™ comes in.
With Nfina-View’s Summary view, you can see the health of your IT ecosystem at a glance. Quickly view zones, clusters, and node details such as status, IP address, uptime, memory health, CPU utilization, memory and DiskPool information. Hardware details provides information on the health of the power supplies, fans, motherboard voltages, and hard drives. Storage Pool details provide information for the storage pool status, capacity, Zvols, datasets, read cache, snapshots, and clones. Network details display the host name and interface details such as IP address, MAC address, speed, model, Tx/Rx errors, drops, and status. All sensor readings are reported, and any errors trigger alerts can be set to notify administrators of a potential issue.
Another important aspect is ensuring data replication across multiple nodes. You need to make sure that replicas are synchronized and up-to-date with the master node in case of any failover scenarios. Regular backups are crucial as well, especially before performing any maintenance activities or upgrades on the cluster. These backups should be stored off-site in case of disasters such as floods or fires. Nfina-View™ removes complexities associated with shifting workloads from one site to another by incorporating site-to-site Failover and Rollback operations. If the primary file system fails or a proactive shift of your workloads is necessary, you can Failover and restore operations at a secondary location to keep downtime at a minimum. Nfina-View™ includes the ability to restore entire file system states to an earlier point in time using built in Rollback functionality. This is especially useful during a ransomware attack which has corrupted the IT ecosystem withing network attached storage. During a ransomware attack, the rollback functionality can have all the customers data availability back online within minutes of performing the rollback operation.
Security measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection, and backup testing systems should also be implemented to protect against cyber threats like hackers and malware attacks. Nfina-View™ includes automated disaster recovery testing that easily allow administrators to power on and connect to virtual machines in the DR location. While most organizations have backups, they seldom fully test their backups. Backups are a great to have, but they are only useful if they are functional and can be quickly deployed if a disaster occurs. Nfina-View’s disaster recovery testing allows you to test your backups in their location, giving you peace of mind ensuring that your systems will be restored if needed. Not every situation involves complete restoration of entire file systems. Often, restoration of singular virtual machines or even file level restores within a virtual machine need to be performed. Instant clones from file system immutable snapshots allow for quick and easy machine and file level restorations.
FAQ
How is clustered storage updated? | The Clustered Storage system is updated through a specialized tool called a cluster-aware updating (CAU) tool. This tool allows individual nodes within the cluster to be updated without taking the entire system offline, ensuring high availability and uninterrupted performance for applications. Additionally, our Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV) technology allows multiple nodes to access the same storage simultaneously, making it ideal for running virtual machines. With this efficient and streamlined process, you can trust that your clustered storage will always be up-to-date and running smoothly.
How do I configure clustered storage? | Configuring clustered storage is a simple and straightforward process. First, you will need to set up the servers that will be sharing access to the storage pool. This can typically be done through a user-friendly interface or by following step-by-step instructions provided by our team. Once the servers are set up, you can then allocate storage space from the pool to each server based on your specific needs. Our system also allows for easy scalability, so you can add more servers or storage space as your needs grow. With our intuitive system and helpful support team, configuring clustered storage has never been easier.
Is clustered storage suitable for everyday use, like storing photos or documents?
The intricacy, expense, and operational demands of clustered storage make it unsuitable for most individuals. Essentially configured for an enterprise with extreme scalability needs, high performance, and constant availability of data.
How can using clustered storage improve the reliability of my files and applications?
Data replication across numerous nodes allows the system to automatically change to another node if one fails which allows the system to avoid downtime and loss of data. This guarantees data availability and security against hardware and software problems. Additionally, it enables the system seamless scalability and load balancing to optimize performance.

At Nfina, our Eco-Friendly Solutions make it easy for our customers to achieve a lower carbon footprint and play a positive role in bringing about a sustainable future. We design technologies and products to help people understand their impact and actions better.
Nfina’s Hybrid Cloud and Hyperconverged solutions provide energy efficiency by using high-density, lower-power VMs enabling our customers to scale their digital transformations sustainably by optimizing space, reducing power consumption, and lowering cooling and maintenance costs. Nfina is taking a leadership role in doing what it takes to tackle climate change.
Nfina has been carbon neutral for our operations since opening in 2012.
